| Welcome to the Beginner's Guide to Aerodynamics | ||||
 |
||||
| What is aerodynamics? The word comes from two Greek words: aerios, concerning the air, and dynamis, which means force. Aerodynamics is the study of forces and the resulting motion of objects through the air. Judging from the story of Daedalus and Icarus, humans have been interested in aerodynamics and flying for thousands of years, although flying in a heavier-than-air machine has been possible only in the last hundred years. Aerodynamics affects the motion of a large airliner, a model rocket, a beach ball thrown near the shore, or a kite flying high overhead. The curveball thrown by big league baseball pitchers gets its curve from aerodynamics. | ||||
|
At this Web site you can study aerodynamics at your own pace and to your own level of interest. Some of the topics included are: Newton's basic equations of motion; the motion of a free falling object, that neglects the effects of aerodynamics; the terminal velocity of a falling object subject to both weight and air resistance; the three forces (lift, drag, and weight) that act on a glider; and finally, the four forces that act on a powered airplane. Because aerodynamics involves both the motion of the object and the reaction of the air, there are several pages devoted to basic gas properties and how those properties change through the atmosphere. There is a special section of the Beginner's Guide which deals with compressible, or high speed, aerodynamics. This section is intended for undergraduates who are studying shock waves or isentropic flows and contains several calculators and simulators for that flow regime. . There are many pages here connected to one another through hyperlinks and you can then navigate through the links based on your own interest and inquiry. There is an Aerodynamics Index of topics that you 
| ||||
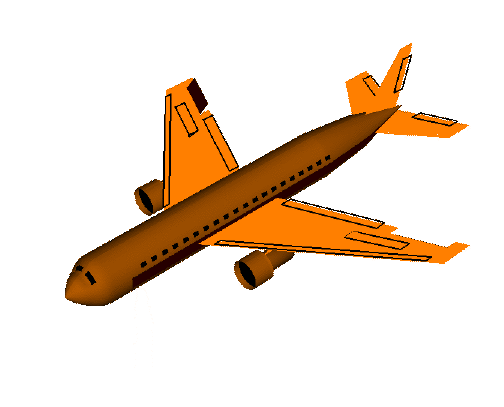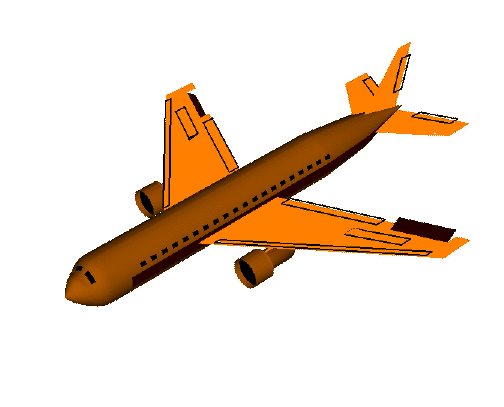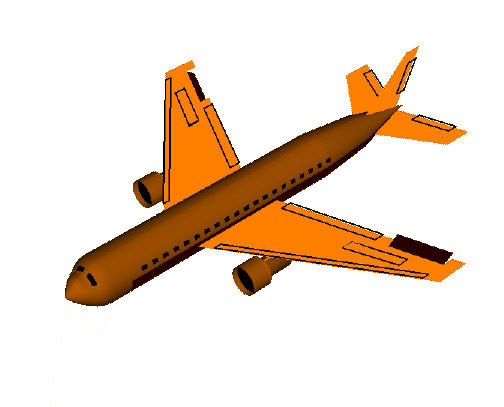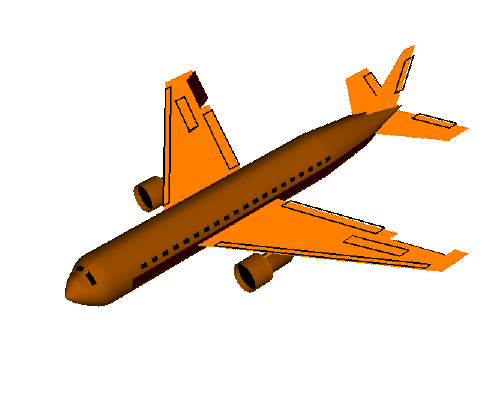
Airplanes Parts of a Plane The body of the plane is called the fuselage . It is generally a long tube shape. The wheels of a plane are called the landing gear . There are two main wheels on either side of the plane fuselage. Then there is one more wheel near the front of the plane. The brakes for the wheels are like the brakes for cars. They are operated by pedals, one for each wheel. Most landing gear can be folded into the fuselage during the flight and opened for landing. All planes have wings . The wings are shaped with smooth surfaces. The smooth surfaces are slightly curved from the front or leading edge, to the back or trailing edge. Air moving around the wing produces the upward lift for the airplane. The shape of the wings determines how fast and high the plane can fly. A cut through the wing from front to back is called an airfoil . The hinged cont...
its nice
ReplyDelete